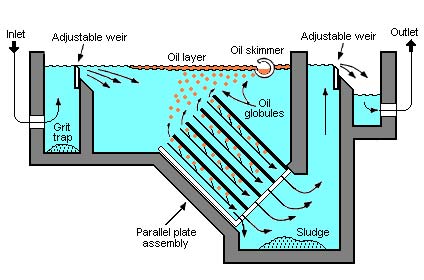
API separator
In wastewater treatment, an API separator refers to an “API Oil-Water Separator.” It is a specific type of equipment used to separate and remove free oils and suspend solids from wastewater.The primary function of an API separator is to separate and remove oil and grease from the wastewater before it undergoes further treatment processes.
Process Steps & Various Functions
Inlet Zone: The wastewater enters the API separator, and its flow velocity is reduce, allowing the separation process to occur.
Oil-Water Separation: Due to the difference in density, lighter oils and greases float to the surface, forming a layer of “float” or “skim” on top of the water. This layer is continuously skimmed off using a mechanical skimmer or an overflow weir.
Settling Zone: Heavier solids and sediment settle to the bottom of the separator, forming a sludge layer. Sludge is periodically remove from the separator for further treatment or disposal.
Outlet Zone: Vartially clarified water, with reduced oil and solids content, exits the separator through an outlet.
Process Mechanism
The separator operates base on the principle of gravity separation, taking advantage of the differences in density between oil, water, and solids.
Design Features
API separators may include various design features to enhance their efficiency, such as baffles and weirs that promote longer residence time and improve separation. Additionally, coalescing plates or media may be install to facilitate the coalescence of smaller oil droplets, aiding their separation from the water.
Overall, micro screens play a vital role in wastewater treatment by providing an additional level of filtration to ensure the removal of very fine particles, suspend solids, and microorganisms, thus improving the overall water quality and protecting downstream treatment processes and equipment.
Targeted Impurities
- Free Oil & Greases
- Floating Oil
- Suspend Solids