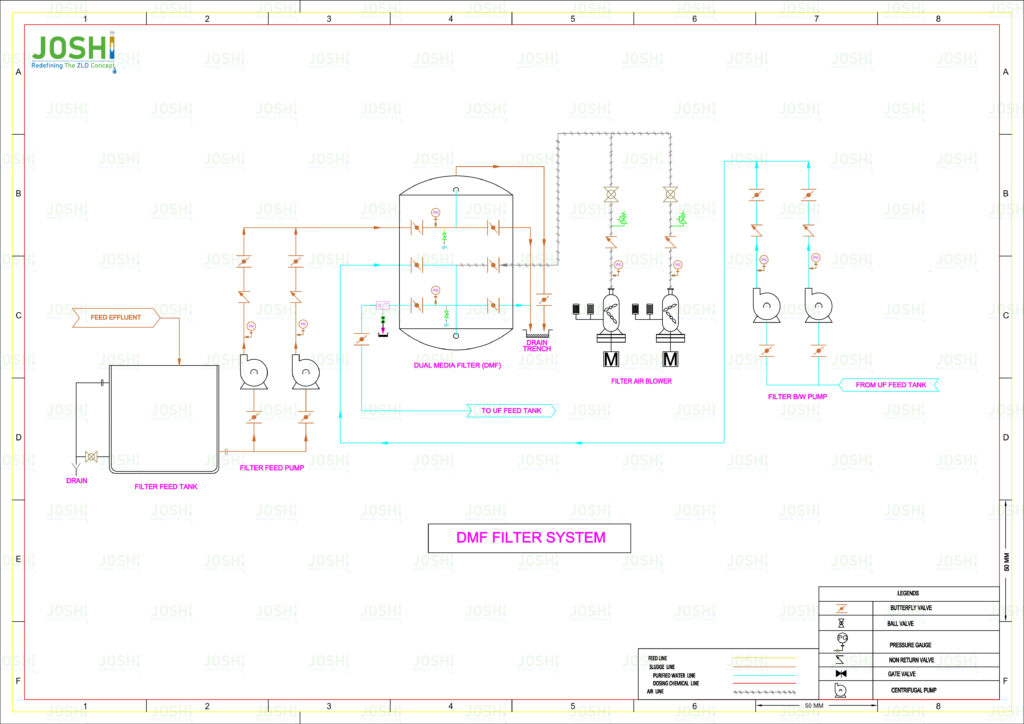
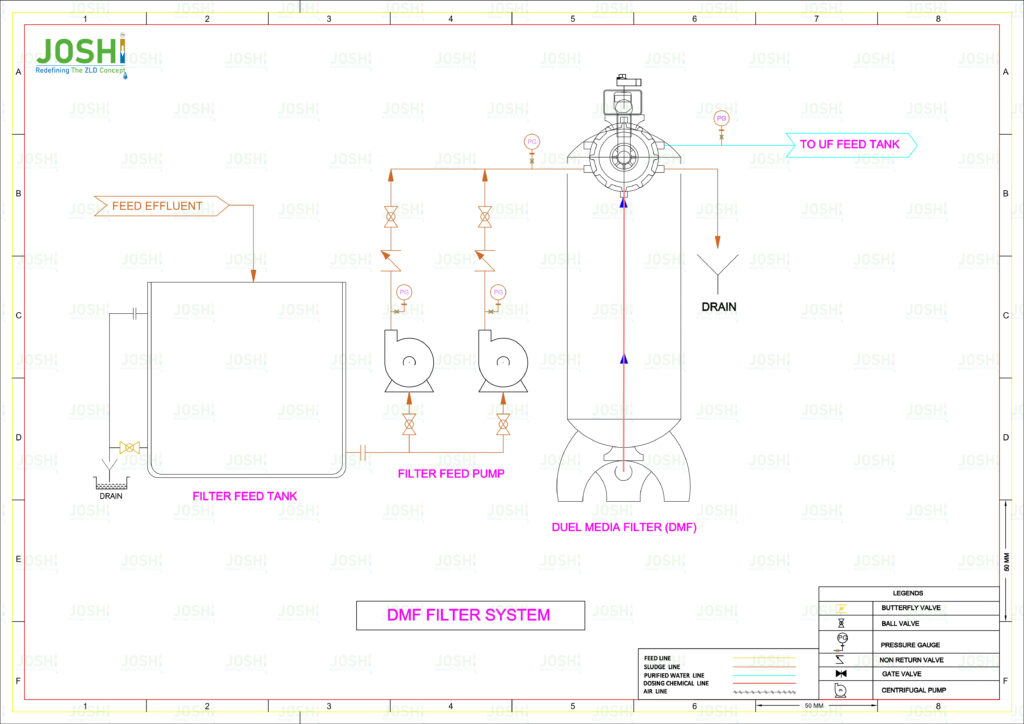
DMF - Dual Media Filter
A dual media filter, also known as a multimedia filter, is a type of filtration system use in wastewater treatment to remove suspend solids and fine particulate matter from water. It is designed to provide enhance filtration performance compared to single media filters by utilizing a combination of two or more distinct filter media with different particle sizes.
System Components
Filter Vessel: The filter vessel is a cylindrical or rectangular tank that contains the filter media. It is designe to withstand the operating pressure of the system. The vessel is usually made of steel or reinforc concrete and is equippe with inlet and outlet connections.
Filter Media: The dual media filter utilizes two or more layers of different filter media with varying particle sizes. The media layers are arrange in a specific sequence within the filter vessel. Common combinations include anthracite coal and silica sand, anthracite coal and garnet, or anthracite coal, sand, and gravel. The larger media, such as anthracite coal or garnet, are place at the top, while the finer media, such as silica sand, are position at the bottom.
Distribution System: The distribution system ensures even distribution of the influent wastewater across the filter media bed. It typically consists of underdrains, lateral pipes, and nozzles that distribute the water uniformly over the surface of the media.
Backwash System: A backwash system is incorporat in the dual media filter to periodically clean the filter media and remove accumulate solids. It includes a backwash pump, valves, and a wash water collection system. The backwashing process involves reversing the water flow and fluidizing the media bed to dislodge trap particles.
Control System: A control system monitors and regulates the operation of the dual media filter. It controls flow rates, backwashing cycles, and other parameters to optimize the filtration process and ensure efficient operation.
Process Description
Filtration: The influent wastewater enters the filter vessel through the inlet connection and is evenly distribute across the top layer of larger media by the distribution system. As the water flows through the media layers, suspend solids and particulate matter are trappe within the filter.
Particle Capture: The larger media at the top layer act as a pre-filter, removing larger particles and providing a protective layer for the underlying finer media. The finer media in the lower layers provide additional filtration and capture smaller particles.
Accumulation of Solids: Over time, the suspend solids accumulate in the filter media bed, causing an increase in pressure drop across the filter. This indicates for backwashing to restore the filter’s efficiency.
Backwashing: When the pressure drop reaches a predetermined level, the control system initiates a backwash cycle. The backwash pump reverses the water flow, fluidizing the media bed from the bottom to the top. This action dislodges and removes the trappe solids, which are carried out through the wash water collection system.
Rinse and Return to Service: After backwashing, a rinse cycle may be performe to settle the filter media and remove any remaining impurities. The filter is then return to the filtration mode, and the cycle continues.
Significance & Advantages
Enhanced Filtration Performance : The combination of different media with varying particle sizes provides improv filtration efficiency and a higher solids removal capacity compared to single media filters.
Extended Filter Run Time: The dual media configuration allows for longer filter run times between backwashing cycles, reducing operational costs and water consumption.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Different combinations of media can be use to tailor the filtration system to specific wastewater characteristics and treatment goals.
Targeted Impurities
- TSS
- Turbidity