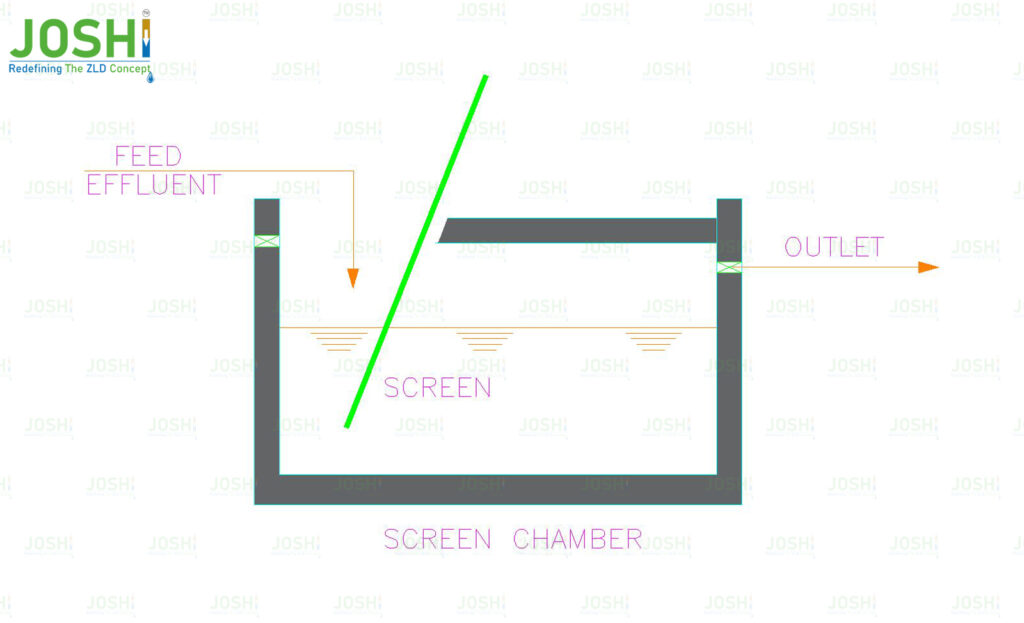
Coarse Screen
In wastewater treatment processes, a coarse screen refers to a mechanical device used to remove large solid materials and debris from the incoming wastewater stream. It is the initial stage of the treatment process and serves to protect downstream equipment, such as pumps, valves, and fine screens, from damage or clogging caused by large objects.
System Components
The coarse screen typically consists of a series of parallel bars or rods space apart to allow the passage of water while retaining larger objects. The spacing between the bars or rods can vary depending on the specific application and the size of the materials expected to be encountered. Common bar spacing ranges from 10 to 150 millimeters.
Process
As wastewater flows through the coarse screen, solid materials such as sticks, rags, plastics, leaves, and other debris are trappe on the screen’s surface (surface straining). Periodically, the accumulated material is removed manually or by using mechanical rakes, conveyor belts, or rotating drums. The remove debris is then typically dispose of or sent for further treatment and processing.
Significance & Advantages
The coarse screen is an essential component in wastewater treatment plants as it helps prevent damage to downstream equipment, reduces the risk of clogging in pumps and pipes, and ensures the effective operation of subsequent treatment processes.
Targeted Impurities
- Coarse Solids – sticks,
- rags & debris,
- fine solids,
- small particles,
- floatable matter
- algae.